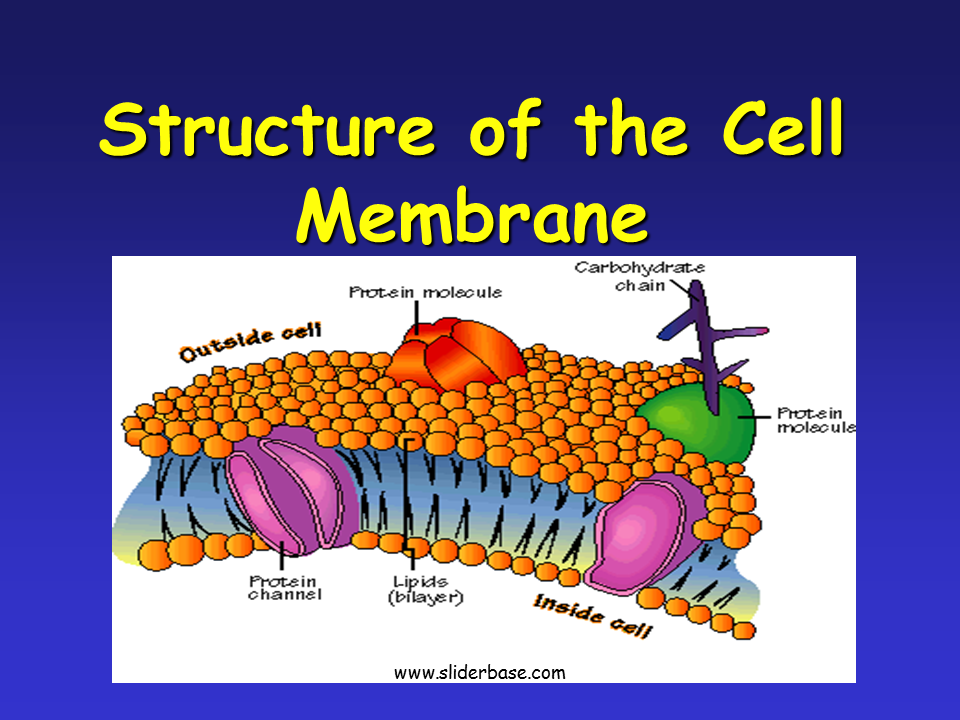
Get Cell Membrane Structure And Function Ppt Pics Function of cell membrane 16 17. Adhesion between cells reception of signaling molecules cell to cell recognition plasma membrane structures * 4.
Part 1 Structure And Models Of Biological Membranes Ppt Download from images.slideplayer.com
Cell membrane structure and function. Boundary around the plant cell outside of the cell membrane that provides structure and support. The cell becomes flaccid (limp) and if enough cells are flaccid, the plant will wilt.
Glucose transporter) 2) receptor proteins:
Likewise the cell membrane is a thin, flexible layer Cell structure and function * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * cells smallest living unit most are microscopic principles of cell theory all living things are made of cells smallest living unit is the cell all cells arise from preexisting cells (this principle discarded the idea of spontaneous generation) cell types prokaryotic eukaryotic prokaryotic cells first cell type on earth cell type. Carbohydrate chains glycoproteins and glycolipids only occur on outside surface of cell membrane function: Life at the edge • the plasma membrane is the If it is alive, it has cells! Oxygen and carbon dioxide can pass easily water can freely cross the membrane 17 18. Cell membrane structure (1.3) ib diploma biology essential idea: The structure and function of the cell membrane ppt notes cells function similarly in all living organisms the cell membrane is kind of like a soap bubble. Membrane structure and function all cells have a plasma or cell membrane , which contains the cell. Cell volume electronic response of neurons and muscle cells transport of sugars, amino acids via 2ndary active transport. Membrane structure and function (problems: The phospholipid bilayer the plasma membrane is common to all cells separates: Function of cell membrane 16 17. Scanning electron micrograph (sem) of adipocytes (ad) membrane structure and function prokaryotic cells: Likewise the cell membrane is a thin, flexible layer that seals the inside of. View chapter 4 (membrane structure and function).ppt from biology microbiolo at zarqa private university. Definition of cell a cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. A soap bubble consists of a thin, flexible _____. External surface lined with hydrophilic polar heads Membrane structure and function.ppt author: Cell membrane structure and function 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells the cell is the basic unit of all organisms all cells come from cells two types of cells parts in common cell membrane cytoplasm organelles dna need volunteers owner of a restaurant 1 waiter need 6 guests this is a. Adhesion between cells reception of signaling molecules cell to cell recognition plasma membrane structures * 4. Cell membrane structure and function. Osmosis is a kind of diffusion. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. Likewise the cell membrane is a thin, flexible layer Internal living cytoplasmic from external environment of cell phospholipid bilayer: Cell membrane, cell transport & cell division chapter 7: • learn the fluid state of membranes and the movement of its lipids and proteins. Jacksonchapter 7membrane structure andfunction lectures by erin barley kathleen fitzpatrick© 2011 pearson education, inc.
Source: image.slidesharecdn.com
• learn the fluid state of membranes and the movement of its lipids and proteins.
Source: slideplayer.com
Osmosis is a kind of diffusion.
Source: image3.slideserve.com
Life at the edge • the plasma membrane is the
Source: i.pinimg.com
• learn the fluid state of membranes and the movement of its lipids and proteins.
Source: i.pinimg.com
Na+ channels) b) carrier proteins (e.g.